Euro-zone economies
欧元区经济
Mirabile dictu
说也奇怪
A recovery at last, but no revelation
终于有所复苏,但是也不出乎意料
Aug 17th 2013 |From the print edition
THE prayed-for recovery in the euro area has finally come to pass. After a dismal 18 months in recession, euro-zone GDP rose by 0.3% (an annualised rate of 1.1%) in the second quarter from its level in early 2013. That outcome was a bit stronger than expected, although the outlook for growth remains weak.
欧元区祈求已久的复苏终于来了。经历了十八个月低沉的衰退之后,相比2013年第一季度,欧元区的GDP在第二季度增加了0.3%(年化增长率为1.1%)。这个表现强于预期,尽管增长的前景仍然堪忧。
The upturn was led by Germany, whose GDP increased by 0.7%. France did surprisingly well, with output up by 0.5%. There was also some encouraging news from southern Europe. Output continued to fall in Italy and Spain but the rate of decline slackened to 0.2% and 0.1% respectively. And there was a sharp rebound in Portugal, which has suffered a deep recession: its GDP grew by 1.1%.
这次回升由德国主导,其GDP增长了0.7%。法国的表现有点出乎意料,增长了0.5%之多。南欧也有好消息。尽管意大利和西班牙的GDP继续下滑,但是各自只下滑了0.2%和0.1%。而葡萄牙则有一个剧烈的反弹,之前经历了很严重的衰退,而现在GDP增长了1.1%。
The pickup still leaves GDP across the euro area 0.7% lower than a year ago. The output declines since the second quarter of 2012 have been biggest in tiny Cyprus, where GDP is down by 5.2%, and in Greece, where it has fallen by 4.6%. Despite its performance in the second quarter, the Portuguese economy is 2% smaller than a year ago.
欧元区经过此次回暖之后,GDP总量仍然比去年低0.7%。自去年二季度到现在衰退最严重的是小国塞浦路斯,GDP下降了5.2%,而希腊也下降了4.6%。尽管葡萄牙这次表现不错,但是其经济总量与一年前相比也缩小了2%。
The record of the euro-zone economy since the peak reached before the global financial crisis five years ago is even more depressing. Output is 3% lower; in America it is more than 4% higher (see chart). Among the big euro-zone economies only German GDP now exceeds its pre-crisis peak, by 2%. The economies on the periphery of the single-currency club have suffered drastic falls, although Greece is in a league of its own with a shrinkage of 23%.
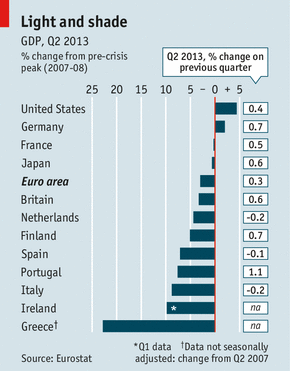
五年前全球金融危机前欧元区的经济达到峰值,从那时到现在的记录更让人失望。工业产出比当时低了3%之多,而美国则高出了4%。在欧元区的经济体中,只有德国现在的GDP总量超过了金融危机前的峰值,比峰值多了2%。欧元区非核心经济体GDP严重下降,虽然只有希腊下降了23%之多。
Even with so much lost ground to make up, the medium-term outlook is for a lacklustre recovery in the euro area, which will continue to be held back by its dodgy banks. Forecasters recently surveyed by the European Central Bank expected on average that euro-zone GDP for the whole of 2013 would be 0.6% lower than in 2012; and that it would grow by only 0.9% in 2014. A tepid recovery is unlikely to do much for the unemployed, especially those in southern Europe where joblessness rates are extraordinarily high. The end of the recession will give fresh heart to European leaders, who can (again) proclaim that the worst of the crisis is over. But weak growth will still leave the euro area vulnerable to social and political discontent.
尽管经济需要重振雄风,但是欧元区的中长期复苏乏力,这其中运转不佳的银行是主要原因。欧洲央行最近调查预测欧元区今年的GDP增量为0.6%,低于去年,而明年的增长率也仅为0.9%,微弱的复苏似乎不能使就业状况好转,尤其是在欧洲南部失业率居高不下的国家。衰退的结束会鼓舞欧盟的领导人,但是谁敢说危机结束了呢?疲软的增势仍然让欧元区极易陷入社会不满与政治不满中。












