This is Scientific American — 60-Second Science. I'm Christopher Intagliata.
As you've probably experienced firsthand, some mosquito species have a real taste for warm, human blood. So much so that if you raise them on in the lab, they'll accept no substitute.
"Fortunately, I don't get major reactions at all." Brad Main is a mosquito geneticist at U.C. Davis... and part-time mosquito meal provider. "So it's not too bad for me. But some people in the lab are itching pretty bad when they have hundreds of mosquito bites on their arms."
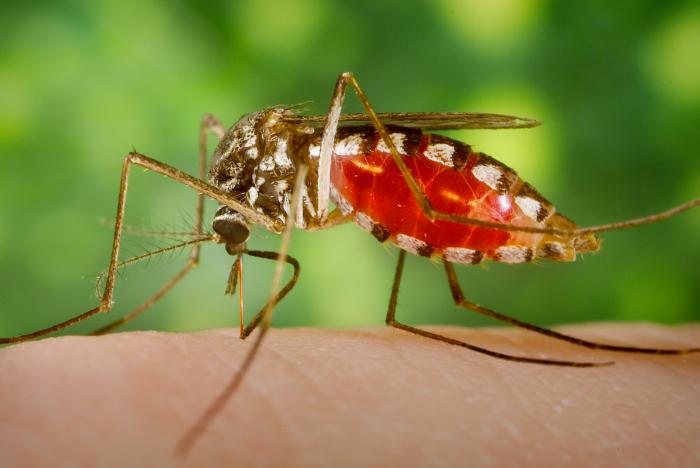
Out in the wild, some species are less picky. Take Anopheles arabiensis, common in East Africa. They'll feed on cattle, dogs, goats, pigs, people—wherever they can find a warm meal. But what Main and his colleagues wanted to know was whether the bloodsuckers' choice of victim might be genetically determined. So they sequenced the genomes of 48 arabiensis mosquitoes from Tanzania which had fed on either humans or cows.
And they found that bugs with cow blood in their bellies had one partially rearranged chromosome, compared to those who'd snacked on human blood... which could explain the preferences in meal choices. The study is in the journal PLoS Genetics.
If that genetic switch really does make cows more attractive than we are to mosquitoes, in theory we could genetically engineer them to steer clear of people. And their cow victims don't get human malaria. "It's a case of knowing your enemy. And so the better we know these mosquitoes, I think the more equipped we're going to be able to control them."
Thanks for listening for Scientific American — 60-Second Science Science. I'm Christopher Intagliata.












