Disease is common, affecting every person at some point in their life. However, there are those unlucky few who contract some the rarer disease—those that seem to do the most damage and are often the hardest to treat, let alone cure. Here are 10 diseases and disorders you really want to avoid.
10.Trigeminal Neuralgia
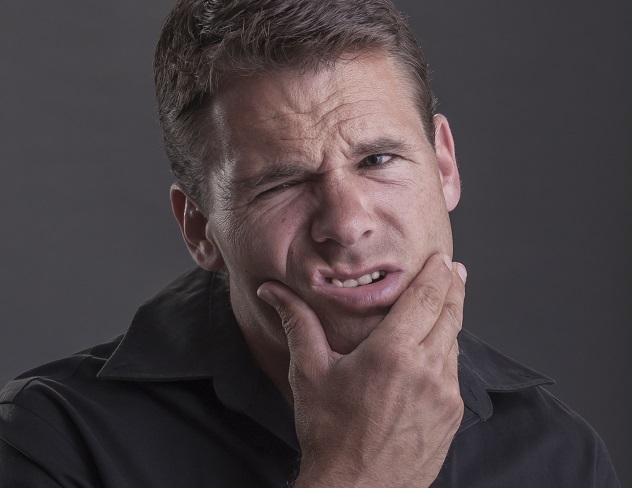

This particular disorder affects the fifth cranial nerve, one of the most widely spread in a person's face. Known to hospitals as the "suicide disease," there are two types. Type 1 is the acute, involving unbelievable pain shooting through the sufferer's face that lasts for as long as two minutes. These attacks can be joined together over a period of two hours of agony.Type 2 is less painful than Type 1, but still one of the hardest hits the human body can take. It is constant, rather than sporadic, with a painful burning or electric shock feeling lasting for years. Regular pain medication like morphine has no effect and anti-convulsion drugs often lose their effectiveness. Various surgical procedures have shown mild success, but are rarely anything more than temporary fixes.
9.Marburg Hemorrhagic Fever
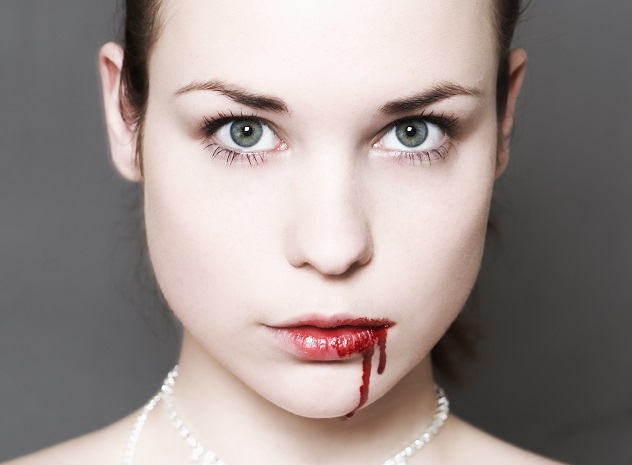

First diagnosed in 1967 after an outbreak in a number of labs throughout Germany and Yugoslavia, Marburg hemorrhagic fever is a disease nearly identical to that caused by the Ebola virus. Monkeys who had been imported from Africa were infected and spread the disease while they were being used for polio research. So far, it is extremely rare, with less than 1,000 cases reported to date, and it's almost always found in Central Africa.The African fruit bat is believed to be the main source of infection, though how it spreads to humans isn't quite known at this point. The initial symptoms are extremely close to much more common diseases such as malaria, so proper diagnosis can be quite tricky. If the infection is severe enough, bleeding in the mouth and rectum and neurologic problems arise. Due to the lack of scientific knowledge about the Marburg fever, there is no established treatment, but plasma and blood protein transplants have shown good results. As of right now, the fatality rate is wide-ranging, ranging from 23–90 percent.
8.Cancrum Oris
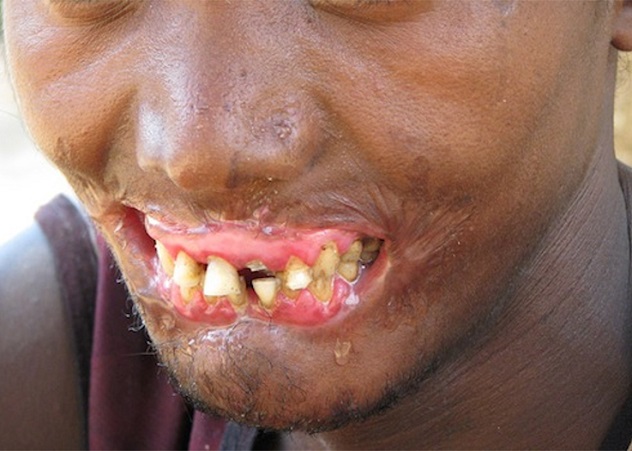
More commonly known as noma, cancrum oris is a gangrenous infection which attacks the facial tissue of its victims, usually children under the age of 6. Especially prevalent in poverty-stricken areas of Africa, not only does the disease have an extremely high fatality rate (80 percent), but those who survive are left horribly disfigured and often ostracized. Affecting nearly 100,000 children every year, the antibodies in the sufferer's body get confused and turn on the soft tissue in the cheek, mouth, and nose.Due to the swift progress of the disease, those infected are quickly disabled, unable to speak or eat normally. The disease has only made brief appearances in Europe and North American since its eradication over 100 years ago, most notably in the Nazi concentration camps. Antibiotics can stop the spread at the first sight of a lesion but they are often unavailable or too expensive.
7.Adhesive Capsulitis
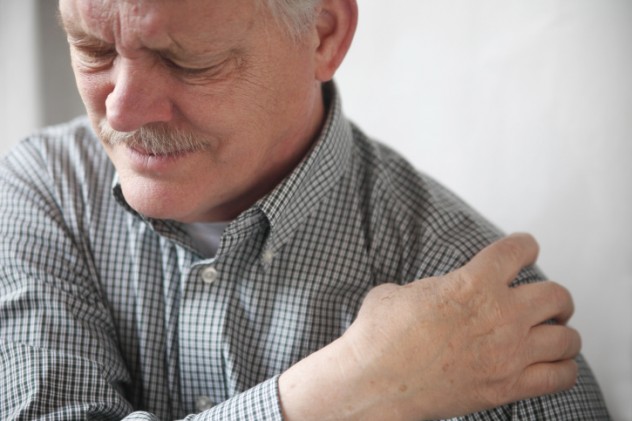
Known by the catchier name of "frozen shoulder," this disorder causes the sufferer's shoulder to become so painful and stiff that it is virtually impossible to do anything with their arm. In addition, sleep can be difficult to come by, causing a myriad other health issues like depression and anxiety. As of now, there is no known cause for frozen shoulder, but diabetes and injuries or surgeries in the area are considered to be risk factors.Frozen shoulder affects an estimated 2 percent of the population at some point in their lives, making it one of the most common disorders on this list, and it is extremely hard to treat. Even with regular medication and constant physical rehabilitation, it can take up to a year to restore mobility. Although there have been cases where it went away on its own, it usually took up to two years to resolve itself.
6.Complex Regional Pain Syndrome
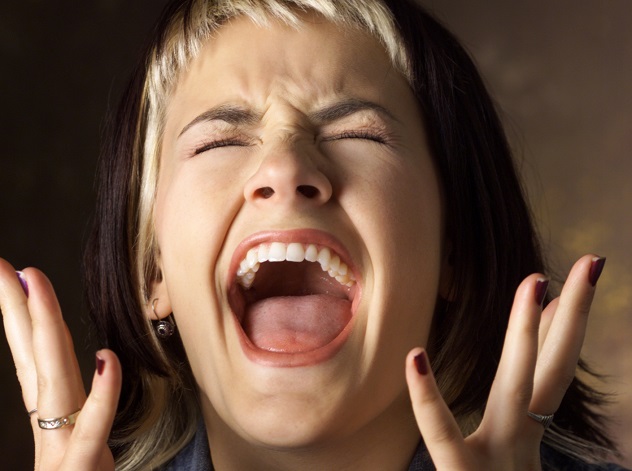

Formally known as "reflex sympathetic dystrophy," CRPS is a lifelong systemic disease which manifests itself as extreme burning pain, bone and skin changes, and unbelievable sensitivity to touch. It's one of the most painful diseases in the world, ranked above childbirth and amputation on the McGill Pain Index, a method of evaluating pain developed in the early 1970s. Initially believed to be a systemic failure of the sympathetic nervous system, researchers now believe it is triggered by trauma, especially to the extremities. However, this is just a guess as of right now, which is one of the reasons there is no cure.Various treatments have achieved a modicum of success, including one brought to us by the wisdom of tech support—"Have you tried turning it off and on again?" In 2003, a 14-year-old girl underwent treatment which consisted of a medically-induced coma with the intent of "resetting" the pain connections in her body. This is generally considered a last-ditch effort, as it carries enormous risk and numerous potential side effects.
翻译:宁舒子 来源:前十网












